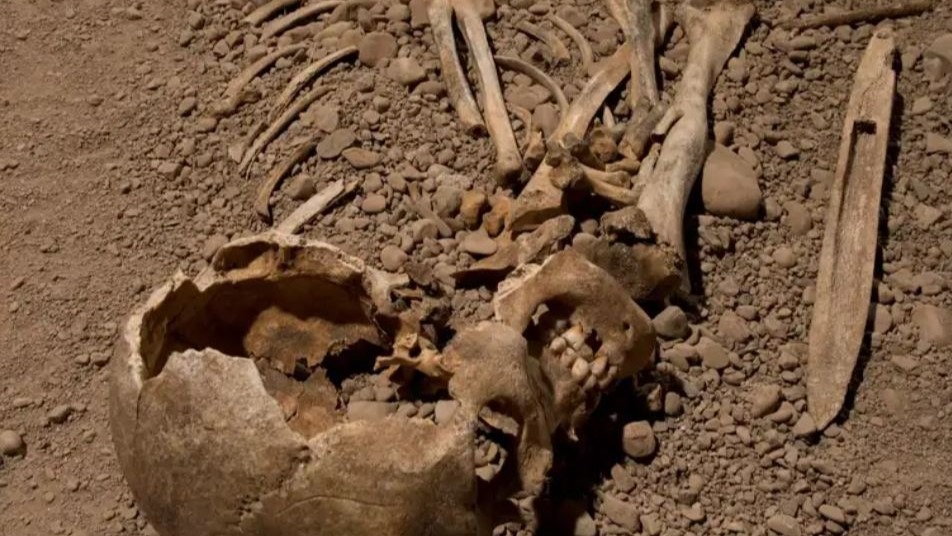
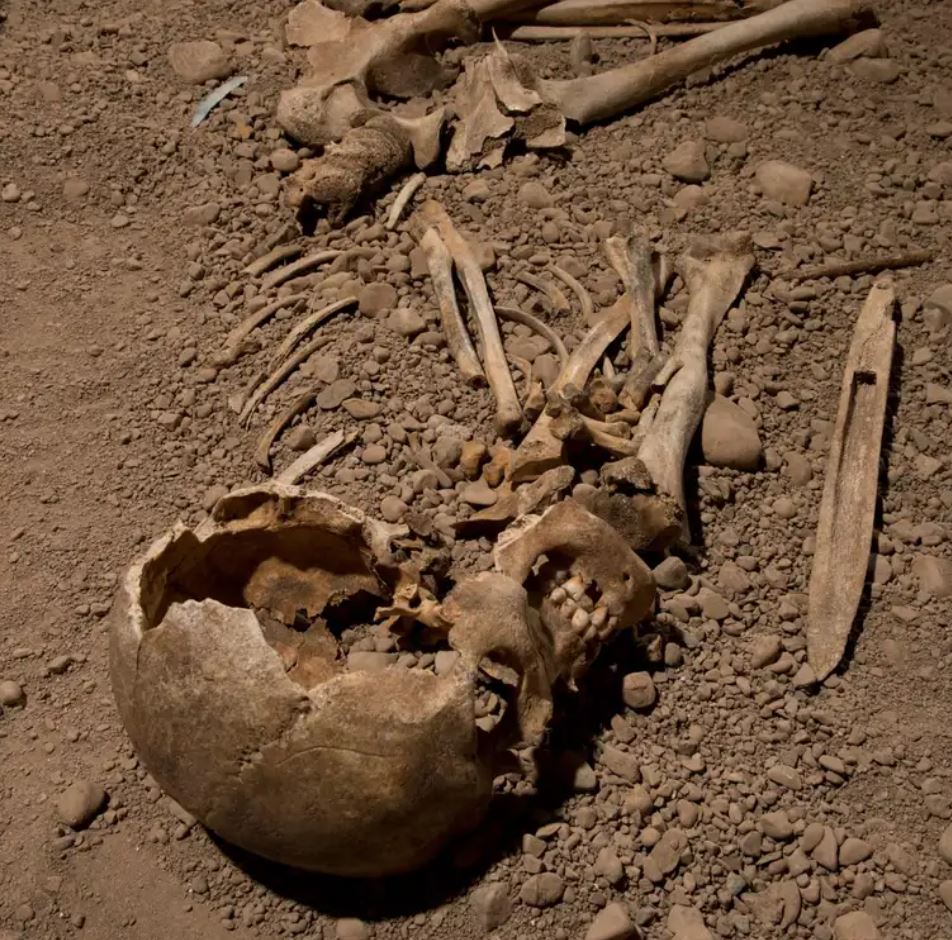
Our study on the Battle Axe Culture by Helena Malmström with others (2019) is published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The study caught the attention of media outlets (“Mysterious ‘Battle Axe Culture’ reveals its secrets thanks to DNA discovery“, by James Rogers, Fox News)

Abstract
The Neolithic period is characterized by major cultural transformations and human migrations, with lasting effects across Europe. To understand the population dynamics in Neolithic Scandinavia and the Baltic Sea area, we investigate the genomes of individuals associated with the Battle Axe Culture (BAC), a Middle Neolithic complex in Scandinavia resembling the continental Corded Ware Culture (CWC). We sequenced 11 individuals (dated to 3330–1665 calibrated before common era (cal BCE)) from modern-day Sweden, Estonia, and Poland to 0.26–3.24× coverage. Three of the individuals were from CWC contexts and two from the central-Swedish BAC burial ‘Bergsgraven’. By analysing these genomes together with the previously published data, we show that the BAC represents a group different from other Neolithic populations in Scandinavia, revealing stratification among cultural groups. Similar to continental CWC, the BAC-associated individuals display ancestry from the Pontic–Caspian steppe herders, as well as smaller components originating from hunter–gatherers and Early Neolithic farmers. Thus, the steppe ancestry seen in these Scandinavian BAC individuals can be explained only by migration into Scandinavia. Furthermore, we highlight the reuse of megalithic tombs of the earlier Funnel Beaker Culture (FBC) by people related to BAC. The BAC groups likely mixed with resident middle Neolithic farmers (e.g. FBC) without substantial contributions from Neolithic foragers.